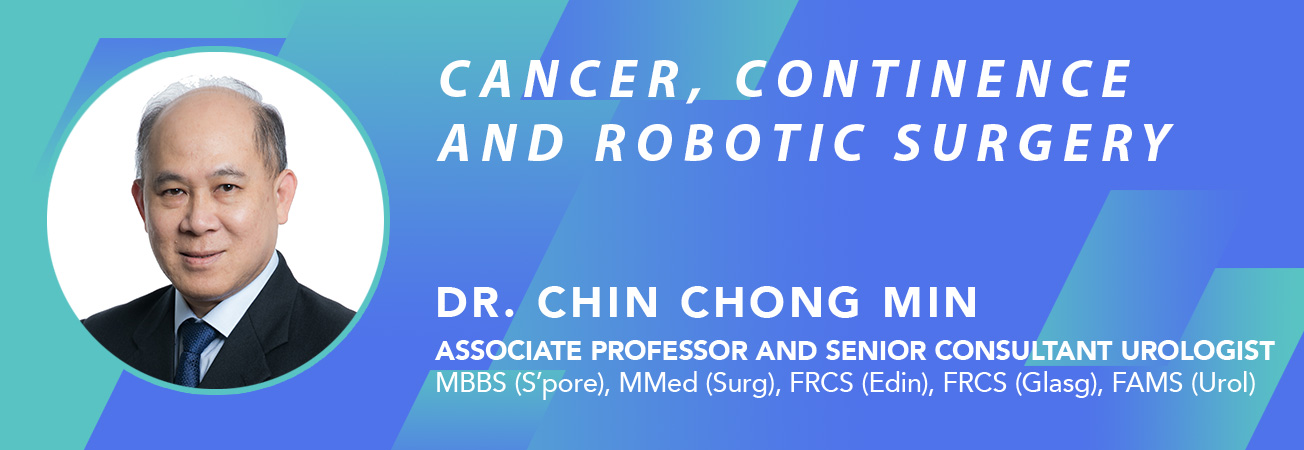
Prostate Biopsy (TRUS or MRI-US fusion Method)
Prostate biopsy is indicated when the PSA (prostate specific antigen) is > 4 ug/L or when an abnormal nodule is felt in the prostate. The role is to rule out cancer and determine its grade. There are two routes by which the biopsy can be done; transrectal route (TR) or transperineal route (TP).
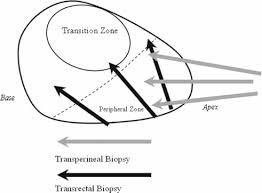
Transrectal vs Transperineal prostate biopsy

Gleason grading system for prostate cancer
TRUS Biopsy
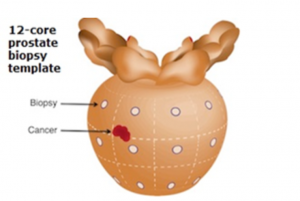
Random biopsy via transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)
This can be done in the clinic under local anaesthesia. An ultrasound probe slightly larger than a finger is inserted into the anus. After measuring the size of the prostate, local anaesthesia is injected around the prostatic nerves. Some 12 biopsies are taken using a small spring-loaded needle. The whole procedure takes 15 to 20 minutes and the histology results should be ready by the 3rd post-biopsy day.
Normally, the accuracy rate of detecting prostate cancer is 80%. This is because the standard 12-core biopsy template can still miss a small cancer, especially if it is in a big prostate. Hence, if the PSA continues to rise, a repeat biopsy may be needed and the MRI-Ultrasound fusion method is preferred.
MRI-Ultrasound Fusion Biopsy
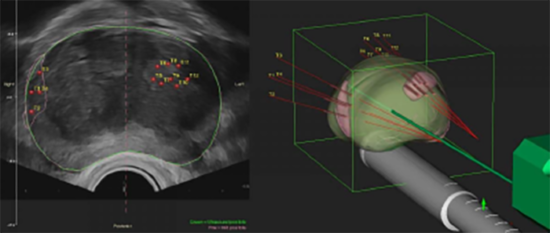
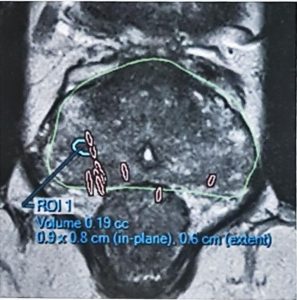
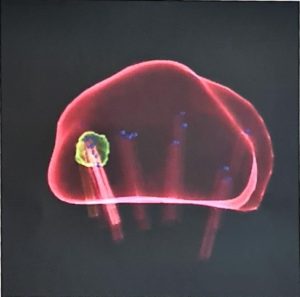
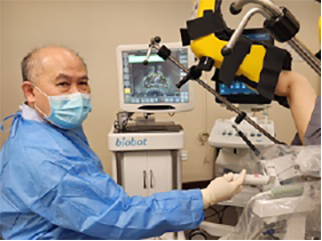
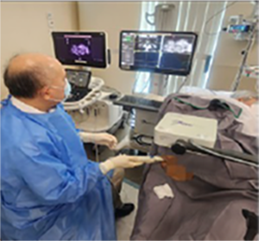
To improve the accuracy rate to 99%, the MRI image can be fused to the TRUS image to target the suspicious area, especially if it is small. The biopsy will be more precise and therefore, less likely to miss the cancer as compared to the standard TRUS method. A software program is employed for fusion-image method and the MRI scan has to be a recent one (taken < 6 months ago). Fusion biopsy costs more because of the equipment and imaging process. As the patient has to stay still throughout the whole procedure, fusion biopsy has to be done under deep sedation. The time needed is longer too, from 30 to 45 mins. To reduce the risk of infection, the transperineal route can be used. The Biobot was developed for this and allows saturation (whole gland) biopsy to be done too.
(a)
(b)
(b)
Targeted biopsy by overlaying the MRI image over the ultrasound image via the a) transperineal route with the Biobot® or b) transrectal route with the UroNav®
(a)
(b)
Dr Chin doing prostate fusion biopsy via the a) transperineal route using the Biobot® & b) transrectal route using the UroNav®
Prostate biopsy does not spread the cancer out of the gland as the sampled tissue is contained within the sheath of the biopsy needle.
Complications include:
- This is more common in diabetics and if there is underlying prostate infection. With antibiotics, the risk of severe infection is reduced to < 5%. The symptoms are burning pain during urination, bloody urine and high fever. Urosepsis will require hospital admission for intravenous antibiotics and resuscitation. The infection rate is much lower if the biopsy is done via transperineal route (<1%)
- bloody urine. This usually clears by the 3rd day but if excessive, the blood clots can block the bladder to cause painful retention of urine. If this happens, catheterisation and washout of the clots is needed
- bleeding from the anus. This tends to occur in those who have pre-existing piles. It usually stops by the next day
- acute retention of urine. This is more likely if the prostate is large, if the patient has untreated BPH and if a lot of samples are taken. It is due to acute prostate swelling which then compresses the urethra to block the bladder. A Foley catheter will need to be inserted if this happens
Desired outcomes:
- minimal pain during biopsy
- minimal anal bleeding
- no clot retention of bladder
- no severe sepsis needing hospitalisation (1% occurrence)