Vasectomy Reversal
Vasectomy reversal can be done as a day case under general anaesthesia using the high-power operating microscope. It takes about 3 to 4 hours, depending on technical difficulty. The operation is performed in one of two ways.
a) Vasovasostomy
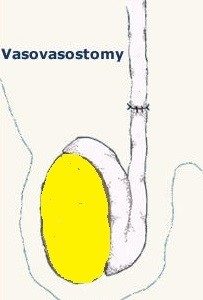
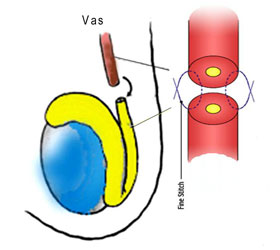
This is the most commonly used technique. The two ends of the vas are isolated. Scar tissue at the vas ends are excised and the fluid from the testicle end is examined for presence of sperms. If the vasal fluid does contain sperm, the two ends of the vas deferens can be joined together. The lumen within the vas deferens is only 0.2 to 0.3 mm in diameter. An operating microscope is used so that fine sutures can be precisely placed; consisting of 6 interrupted sutures in the inner layer to restore continuity and 6 sutures at outer layer to ensure that the repair is leak-proof. Technique is very important because one reason for failure is sperm leakage resulting in inflammation and re-blockage. Hence, the reason for a 2-layer closure.
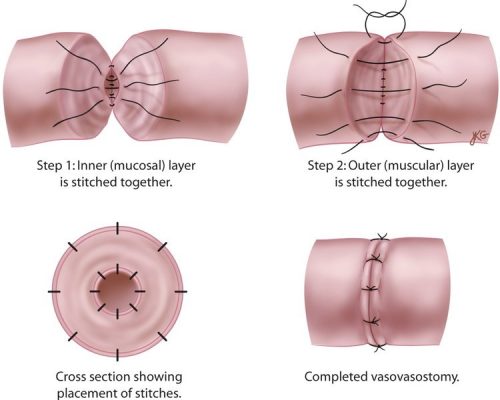
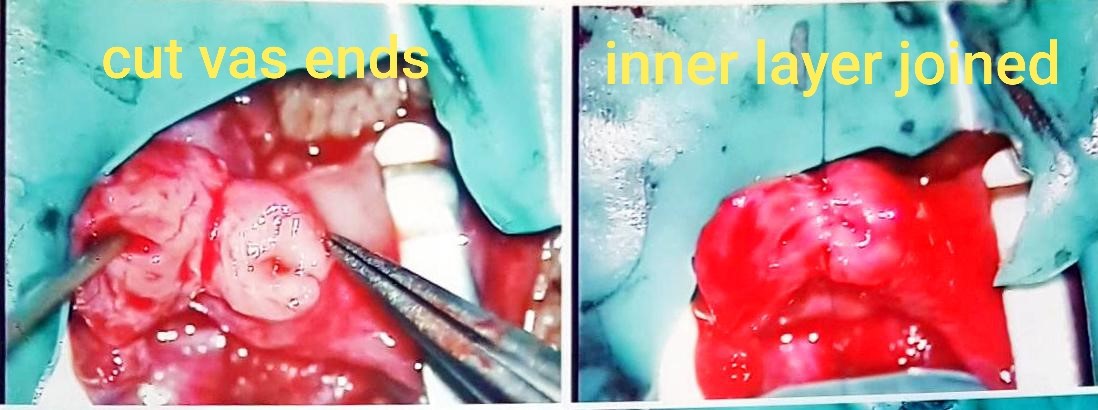
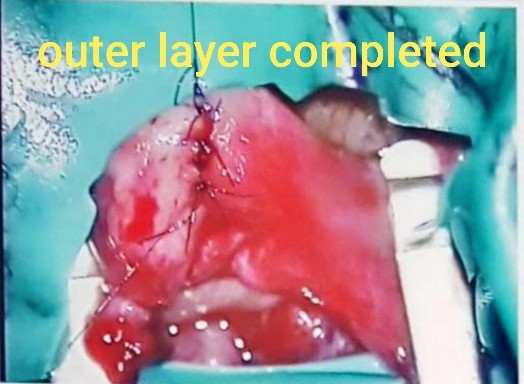
2-layer closure technique
b) Vasoepididymostomy
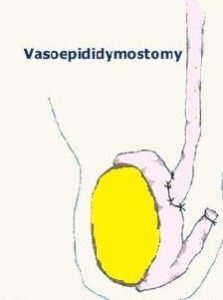
Vasoepididymostomy is a more complicated procedure that involves joining the vas deferens directly to the epididymis. This technique is employed if there is no sperm found at the testicle end of the vas. This technique bypasses any blockage within the vas deferens as a consequence of extensive scarring from the previous vasectomy operation.
The success of vasectomy reversal can be categorized into patency rate (chances of having sperm present after reversal) and pregnancy rate. The patency rate for a vasovasostomy should be about 90%. Patency rate for vasoepididymostomy is lower, around 60%. The pregnancy rate varies widely depending on which procedure is performed, age of the female partner, and the presence of sperm antibodies. In general, vasectomy reversals performed 10 years or more after vasectomy have a lower pregnancy rate.
Complications include:
- scrotal haematoma (blood clot). This is due to excess bleeding and may need surgical evacuation if significant
- infection. The wound or epididymis may be infected, resulting in pain and fever. This will require 2 weeks of antibiotics
- sperm granuloma. This is a small lump that forms when sperm leaks from the vas into the surrounding tissue
Desired outcomes:
- no haematoma
- no infection ( <3% risk )
- success rate > 80% (for cases < 10 years post-vasectomy )