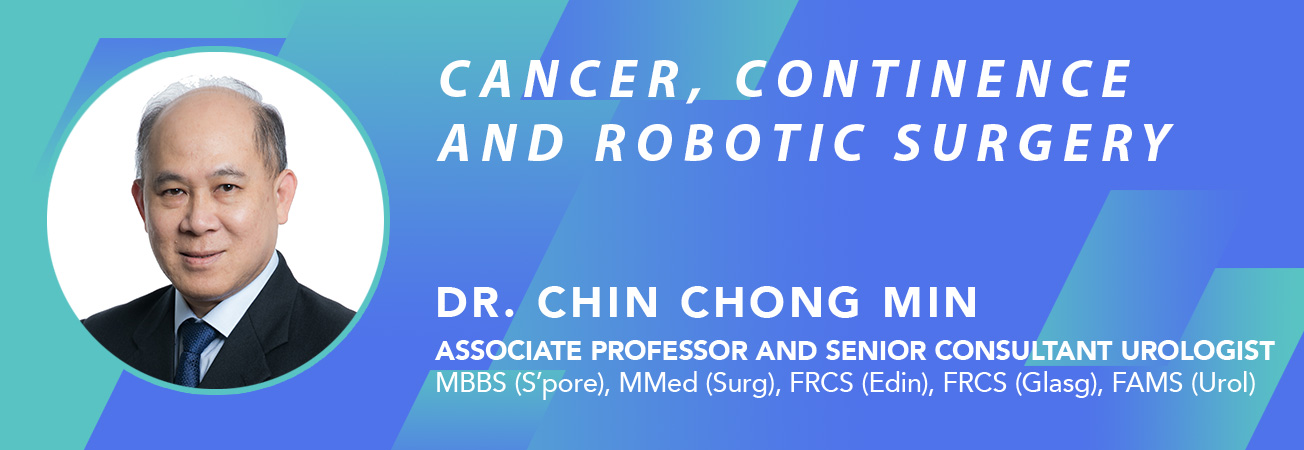
CIRCUMCISION
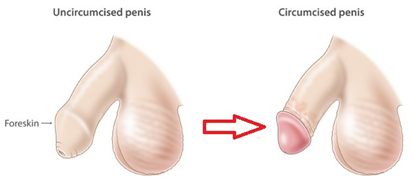
Many boys are born with a tight or excessively long foreskin. Phimosis occurs when the foreskin is long and tight such that it cannot be pulled back to expose the head (glans) of the penis. This can lead to itch, infection (balanitis) and pain / tears during sex. Circumcision is a procedure to remove this excess foreskin.
Phimosis
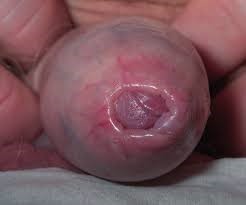
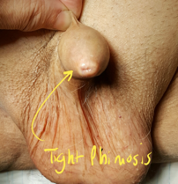
Balanitis from phimosis
How it is done
It is done under general anaesthesia as a day surgery and takes 30 minutes. The excess foreskin is cut off and the edges stitched with sutures that subsequently dissolve. The carbon dioxide laser can also be used, but it is more costly and slower to do.
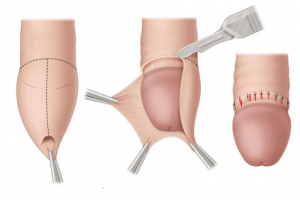
Circumcision to remove excess, tight foreskin

Post-circumcision dressing
The penis is bandaged in a circular manner to control the bleeding and reduce the sensitivity. The circumcision wound heals in 5 to 7 days in children and 8 to 10 days in adults, provided it does not get infected.
Judgment is important in deciding how much foreskin to remove during the surgery; removing too little will require the circumcision to be re-done, while removing too much will result in painful, tight erection.
Complications include:
- Bleeding. If excessive, the bleeding vessel will need re-stitching
- Infection. This will cause pain and can delay wound healing. Hence, it is important to clean the wound daily with anti-septic solution, apply antibiotic cream and complete the antibiotics given
Desired outcomes:
- not too much / not too little foreskin removed
- no active bleeding that require re-stitching (< 1% occurrence)
- wound infection (< 5% occurrence)